What Is Circular Pitch in Gears?
In gear engineering, circular pitch is one of the most fundamental measurements used to describe the spacing of teeth around a gear. It directly affects how gears mesh, transmit motion, and maintain synchronization in power transmission systems. Understanding circular pitch is essential for precise gear design and compatibility between mating gears.
Definition of Circular Pitch
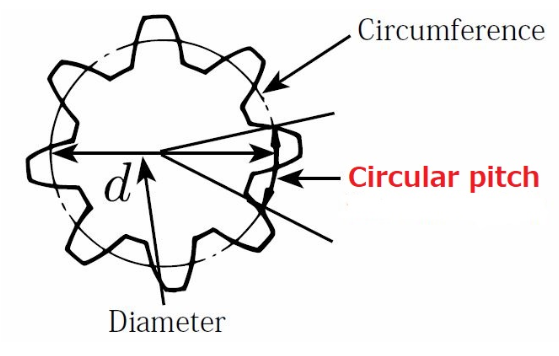
The circular pitch (p) is defined as the distance between a point on one gear tooth and the corresponding point on the next tooth, measured along the pitch circle.
The pitch circle itself is an imaginary reference circle that represents the point of contact between two mating gears.
For two gears to mesh correctly, their circular pitches must be equal ensuring that each tooth on one gear fits perfectly into the space between the teeth on the other.
Formula and Calculation
The formula for calculating circular pitch is derived from the circumference of the pitch circle and the number of teeth: p=πd/N
Where:
-
p = Circular pitch
-
d = Pitch diameter (diameter of the pitch circle)
-
N = Number of teeth
This formula shows that circular pitch depends on both the size of the gear and how many teeth it has — larger gears or fewer teeth result in a larger pitch distance.
Relationship Between Circular Pitch and Diametral Pitch
Circular pitch is closely related to another common gear measurement known as the diametral pitch (P), which is widely used in the imperial system.
Diametral pitch represents the number of teeth per inch of pitch diameter, and the two are mathematically connected as follows: p=π/p
This relationship allows engineers to easily convert between metric-based (circular pitch) and imperial-based (diametral pitch) gear systems.
When to Use Circular Pitch
While diametral pitch is standard in many general gear applications, circular pitch offers advantages in specific cases:
1. Linear Motion Systems (Rack and Pinion):
Circular pitch is ideal for rack and pinion systems, where rotational motion is converted into linear motion. Using circular pitch simplifies indexing and positioning, as each rotation corresponds to a fixed linear distance.
2. Large-Diameter Gears:
For large gears, circular pitch provides a direct measurement of tooth spacing, making it more intuitive and easier to interpret than diametral pitch.
3. Metric-Based Designs:
In metric engineering systems, circular pitch is the preferred unit of measure, providing consistency in gear sizing and calculations.
The circular pitch is a key parameter in gear geometry, determining how teeth are spaced and how smoothly two gears mesh. Precise control of this measurement ensures efficient motion transfer, minimal wear, and reliable performance across mechanical systems.
At Belon Gear, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision gears with optimized tooth geometry—ensuring consistent circular pitch and flawless meshing performance for applications in automotive, robotics, and industrial machinery.
Post time: Oct-29-2025




